Bihar Board Class 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry Ex 3.3 Textbook Questions and Answers.
BSEB Bihar Board Class 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry Ex 3.3
![]()
Question 1.
In which quadrant or on which axis do each of the points (- 2, 4), (3, – 1), (- 1, 0), (1, 2) and (- 3, – 5) lie? Verify your answer by locating them on the Cartesian plane.
Solution:
- In the point (- 2, 4), abscissa is negative and ordinate is positive. So, it lies in the second quadrant.
- In the point (3, – 1), abscissa is positive and ordinate is negative. So, it lies in the fourth quadrant.
- The point (- 1, 0) lies on the negative x-axis.
- In the point (1, 2) abscissa and ordinate are positive, so it lies in the first quadrant.
- In the point (- 3, – 5) abscissa and ordinate are negative. Therefore, it lies in the fourth quadrant.
Let us locate these points on the cartesian plane. Plot the points (- 2, 4), (3, – 1), (- 1, 0) and (1, 2) as shown.
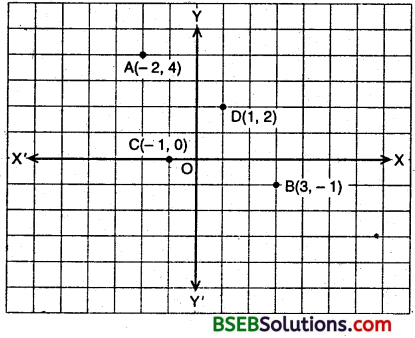
These points are respectively represented by A, B, C and D, which clearly verify their location.
![]()
Question 2.
Plot the points (x, y) given in the following table on the plane choosing suitable units of distance on the axes.
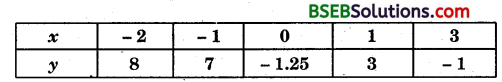
Solution:
Draw X’OX and Y’OY as the coordinate axes and mark their point of intersection O as the origin (0, 0).
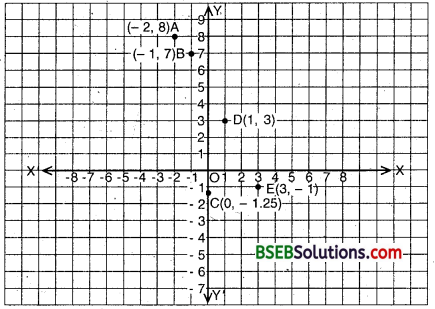
In order to plot the point (- 2, 8), we take 2 units on OX’ and then 8 units parallel to OY to obtain the point A(- 2, 8).
Similarly, we plot the point B(- 1, 7).
In order to plot (0, – 1.25), we’take 1.25 units below x-axis on they-axis to obtain C(0, – 1.25).
In order to plot (1, 3), we take 1 unit on OX and then 3 units parallel to OY to obtain the point D(l, 3).
In order to plot (3, – 1), we take 3 units on OX and then move 1 unit parallel to O’ to obtain the point E(3, – 1).
![]()